The conversations about Bitcoin’s environmental impact are never-ending and they have gathered momentum in the past month. While Bitcoin is at the centre of the storm, it is a challenge that is true to other cryptocurrencies that run on Proof on Work (PoW) like Ethereum.
With decentralization at its core, cryptocurrencies require a network of specialized computers called ‘Mining rigs’ to keep the network running.
Even as talks and efforts are underway to minimize the carbon footprint of Bitcoin, some investors are bullish about green cryptocurrencies like Cardano and Ethereum 2.0 gaining prominence in 2021. Let’s dig further to know if greener solutions are the future of cryptocurrencies.
The Impact of Bitcoin
Around the world, thousands of computers requiring enormous computing power are crushing complex math problems to sustain Bitcoin. Huge amount of electricity is required to complete these transactions – a bone of contention among cryptocurrency critics.
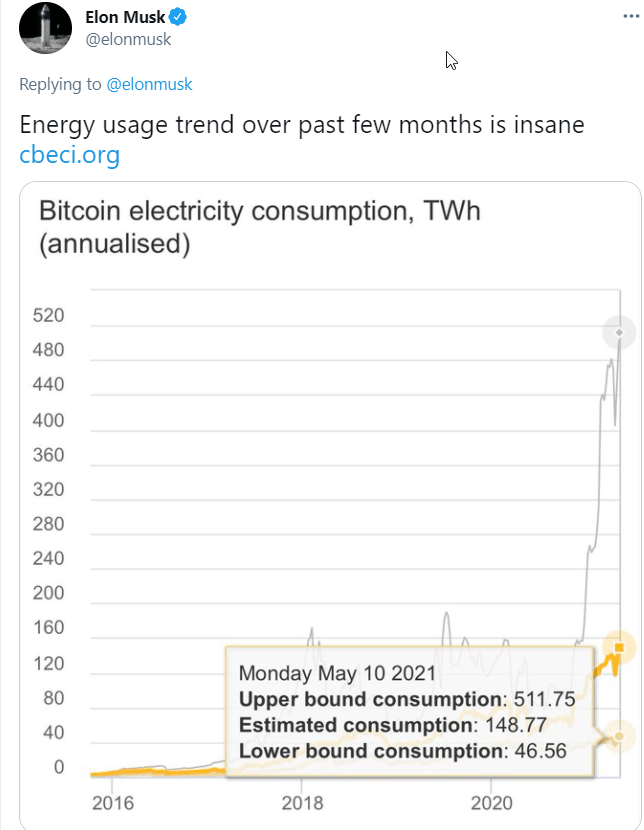
Even though it is difficult to precisely calculate the amount of electricity Bitcoin uses, the community agrees that it is an energy-intensive business. Researchers at Cambridge University suggested that mining for Bitcoin consumes around 121.36 terawatt-hours (TWh) a year, which means it uses more energy than Argentina.
The topic gained headlines in May this year when Tesla CEO Elon Musk said his company would stop accepting Bitcoins for the purchase of vehicles as they use fossil fuels.

Blockchain believers have been suggesting a better way to overcome the environmental implications of Proof of Work (PoW) by paving path for Proof of Stake (PoS).
Also read: What Is Ethereum Gas? Will The Fees Go Down With Ethereum 2.0?
Proof of Work Versus Proof of Stake
To comprehend how PoS is energy efficient, it is important to understand what differentiates it from PoW.
In Proof of Work, multiple parties undertake the task of verifying transactions stored in the blockchain. Thousands of computers around the world participate in this decentralized blockchain verification.
To participate, Bitcoin miners need to use ASIC machines with a significant amount of computing power knows as Hash Rate, equipped with specialized computer chips, semiconductors, a cooling facility a continuous supply of electricity to facilitate the process. The process of verifying the blockchain by the miners is energy-intensive and any cryptocurrency built on Proof of Work will require ‘insane’ use of energy, as Musk says.